General Information About Stroke
Third leading cause of death in USA.
- 25% of deaths after stroke will occur in the first year itself following stroke.
- Strokes are of 2 type
- Hemorrhagic
- Excessive bleeding inside the brain.
- This will be due to leaks from the blood vessels.
- This will be about 15% of all strokes.
- Ischemic
- Lesser blood supply to the brain.
- Usually due to blockage of the vessels (Carotid artery).
- This will be 85% of all strokes.
- Hemorrhagic
A narrowing (Stenosis) will cause blood to jet stream towards the brain and Embloii (small particles of clots) flow towards the brain and may cause
- TIA
- Stroke like symptoms (Speech slur, Weakness, gait (Walking) problems, Tingling in limbs etc.
- With complete recovery inside 24 hrs.
- Symptoms will come rapidly and last for 2 – 15 minutes only.
- Amaurosis fugax
- Transient one sided loss of vision.
- Shadow appearing one quarter, half,, whole eye vision.
- Again will appear suddenly and complete recovery happens inside 1 day usually 2-15 minutes.
- Stroke
- The above mentioned deficit persist after 24 hours.
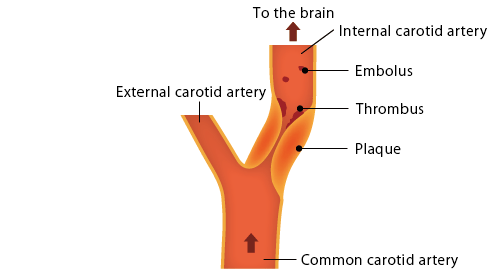
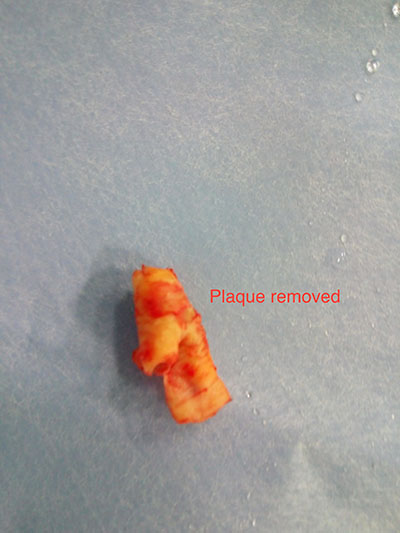
- Plaque = Hard fat+calcium deposit leading to obstruction.
- Thrombus = Clot that remains where it was made, this can further decrease blood flow to the brain.
- Emboli = Clot particle made in the plaque but shoot towards the brain.
- Internal carotid goes to the brain and external carotid towards the face.
What is carotid artery
- It’s the blood vessel that supplies blood to your brain.
- Please see the above picture very carefully.
- Narrowing of the carotid will be causing stroke in about 25% of all stroke incidents.
- Of 100 strokes 85 will be ischaemic and 30% of these 85 ~ 25 will have stenosis of the carotid.
- This means that 25% of all stroke are due to narrowing of your carotid in the neck AND can be prevented if they reach a vascular surgeon in time
- This is the reason why Carotid revascularization (Unblocking of the carotid stenosis) is the MOST COMMONLY PERFORMED VASCULAR SURGERY PROCEDURE
Which patient should be offered carotid revascularization?
- Not all stenosis are for revascularization. If you have survived the first onslaught of the viz TIA, Amaurosis fugax, Stroke our primary aim is the prolong life and prevent further stroke.
- Surgery of the carotid can itself cause stroke that we are trying to prevent. Thus we must compare risk vs benefits of surgery vs best medical practice (This means reducing risk factors and medciations)
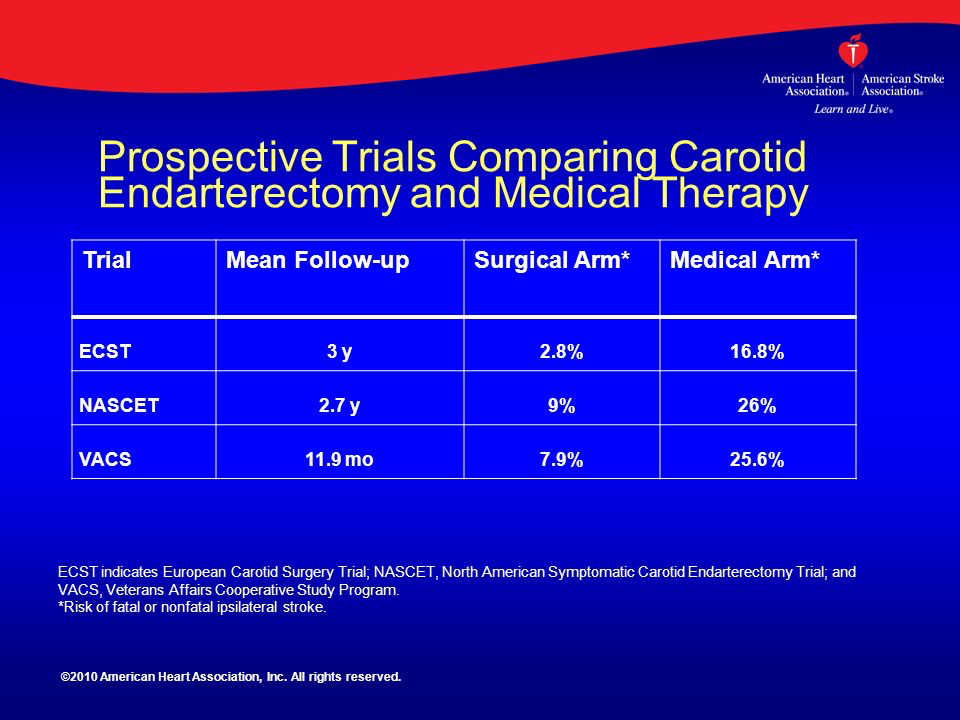
The above chart explains it very clearly
Future risk of NON FATAL stroke in coming 3 years.
- 25% if you are candidate for medical therapy alone.
- 6% if you are candidate for revascularization
YOU WILL HAVE 3% RISK OF IMMEDIATE STROKE IN ANY CAROTID SURGERY.
CANDIDATES FOR CAROTID REVASCULARIZATION ARE
- 70% or more block with or without symptoms.
- 50% - 70% block with symptoms
How is revascularization done
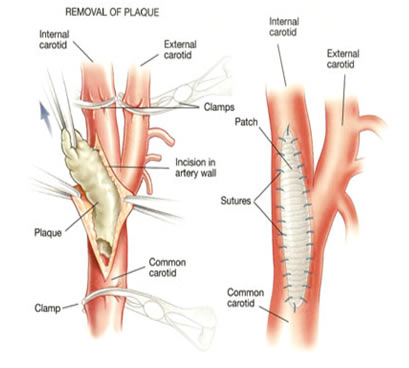
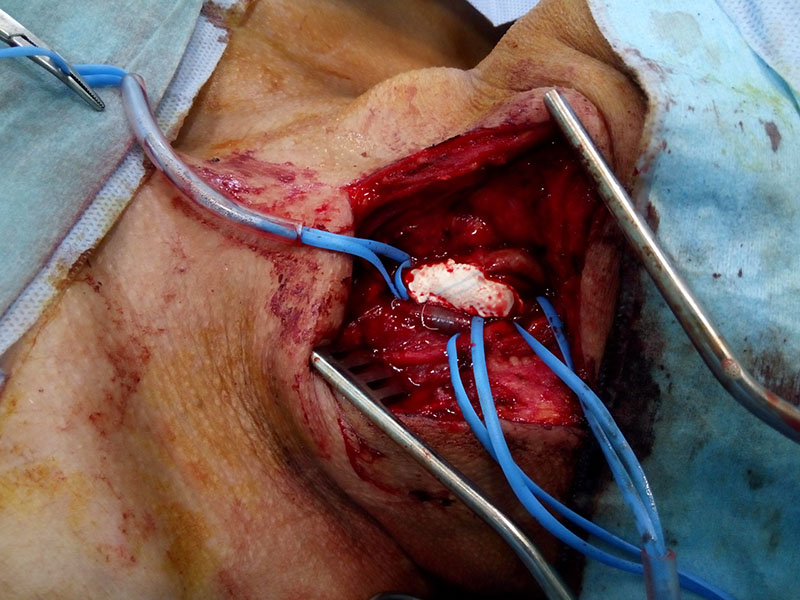
- Carotid endarterectomy
-
- Surgical removal of the block
-
- Endovascular procedures
- Guide wire based widening and stent (frame support placement)
Both procedures will give similar results.
Carotid Endarterectomy is the GOLD STANDARD.
There are specific indications and guidelines for best indications for each procedure.
Professor Digvijay Sharma
Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
